
Ingenieurbüro für angewandte Strömungsmechanik
Contact+ About us
+ News
+ Conferences & Events
- Application Examples
- Introduction
- Automotive Industry
- Bio-medicine
- Bio-technology
- Chemical industry
- Environement
- HVAC & Safety
- Micro-fluidics + MEMS
- Power Stations
- Process simulation
- Turbo-machinery
- Vaccuum technology
- Other examples
+ Imprint
+ Terms of use
Microfluidics and MEMS
FillingMicrocontainers are required to be filled in a certain period of time. Depending on the the interaction between the free surface and the wall bubbles can be entrapped, which can mean a large volumetirc loss. Simulations help find such defficiencies. The surface tension, the static as well as the dynamics contact angles are accounted for. A much too quick filling can be foreseen and adequate adaptations may be investigated before actually making a prototype. The animations shown here indicate the effect of the filling rate on bubble free filling. Alternatively the geometry may be adapted to guarantee bubble free filling at higher filling rates. |
2 µl/min
 Please click for animation (308 kB)
ESC to stop 20 µl/min  Please click for animation (48 kB)
ESC to stop |
ElectroosmosisCourtesy of micronit microfluidics B.V. |
 Please click for animation (495 kB)
ESC to stop |
ElectrophoresisElectrokinetic phenomena are often used to separate different charged particles (e.g. DNA). After separation the different particles may be concentrated to ensure optimal detection. The interaction between the flow field and the potential field is actually an example of multi-physics applications, where several physical phenomena are accounted for at the same time. In the example shown here three particle classes with different charges are being separated and preconcentrated via electrophoresis. After the separation is concluded all particles move at a constant speed (Isotachophoresis). |
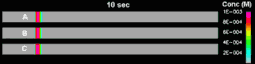 Please click for animation (57 kB)
ESC to stop |
MultiplexerMultiplexers are often used to distribute the flow in preparation for preconcentration and detection of different components (lab-on- chip). The channels are to be filling according to a certain sequence and at a certain speed. This is controlled using microvalves. |
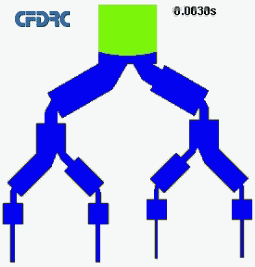 Please click for animation (195 kB)
ESC to stop |
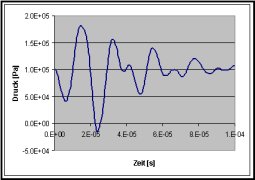
Ink jetsThis example is based on piezo-quartz ink jets. The piezo quartz actuation leads to a resonance within the injector body which presses the ink outwards. The simulation considers:
Because several physical phenomena are accounted for simultaneously this is also a so called multi-physics example. The accuracy of the predicted results is very satisfactory as can be seen in the opposite table. |
 Please click for animation (28 kB)
ESC to stop 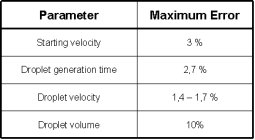 |